The primary use of classes is to bind implementation and data into objects. However, situations arise when you need to expose information about that class of objects without binding it to a particular object instance.
To solve this, PHP allows us to define constants, which is done with the const keyword.
<?php
class User {
const WEBSITE = 'brainbell.com';
}
To access a class constant outside of the class in which it is defined, you must first write the class name, then use the scope resolution operator, which consists of two colons ::, and finally use the constant name. Now, for my preceding example:
<?php
class User {
const WEBSITE = 'brainbell.com';
}
echo User::WEBSITE;
# Prints: brainbell.com
To access a class constant within the class, you can refer to the class name as in the previous code, or you can use the self keyword to tell PHP to look in the current class (or any of the classes whose functionality it extends) for such a constant:
<?php
class User {
const WEBSITE = 'brainbell.com';
public function getWebsite() {
return self::WEBSITE;
}
}
$user = new User();
echo $user->getWebsite();
# Prints: brainbell.com
Constant Arrays
Since PHP 5.6, arrays can be used as plain constants and class constants, consider the following example:
<?php
class User {
const NUMER = ['a', 'b', 'c'];
const ASSOC = ['a'=>'First', 'b'=>'Second'];
}
echo User::NUMER[0]; # Prints: a
echo User::ASSOC['a'];# Prints: First
foreach (User::NUMER as $v)
echo $v . ' '; # Prints: a b c
foreach (User::ASSOC as $v)
echo $v . ' '; # Prints: First Second
Visibility of class constants
Normally, class constants are considered to have a visibility level of public. As of PHP 7.1, you can declare class constants to be public, protected or private.
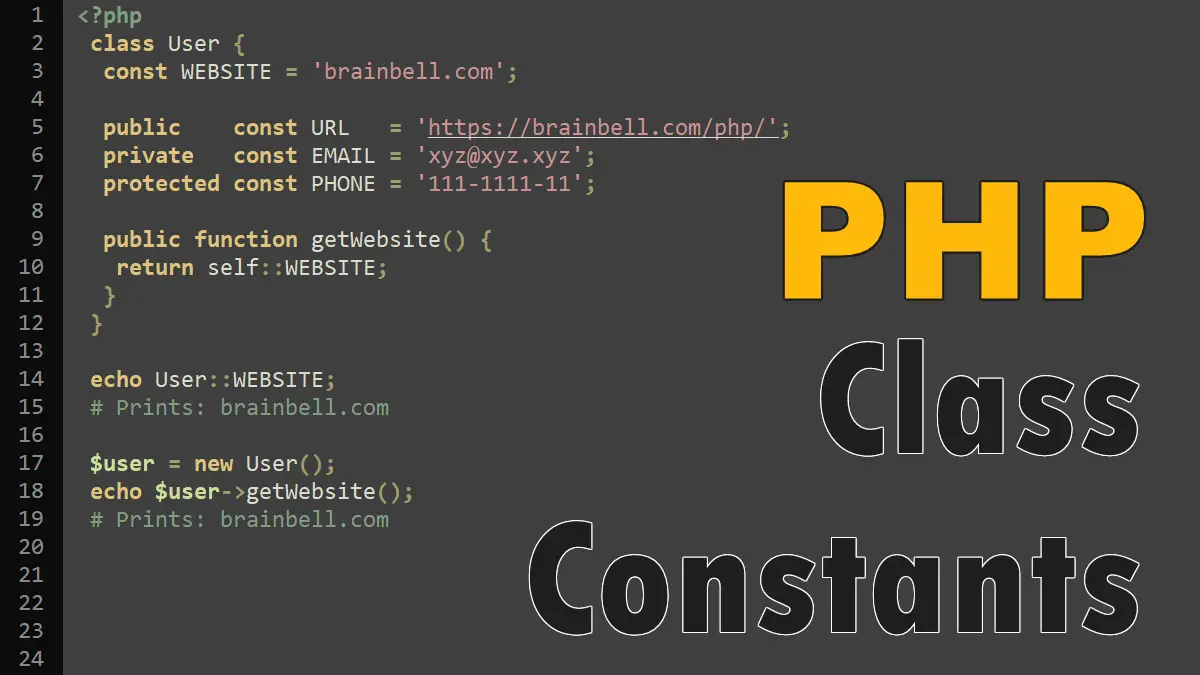
<?php
class User {
# default visibility is public
const WEBSITE = 'brainbell.com';
public const URL = 'https://brainbell.com/php/';
private const EMAIL = 'xyz@xyz.xyz';
protected const PHONE = '111-1111-11';
}
The public, protected and private are the access (visibility) modifiers, for more information read Visibility Modifiers in PHP tutorial.
Note: PHP provides two methods for creating constants: the const modifier and the define function. The const modifier is used to create class constants as described above. The define function can create both global and local constants, but not class constants. See Using Constants in PHP tutorial for details.
PHP OOP Tutorials: