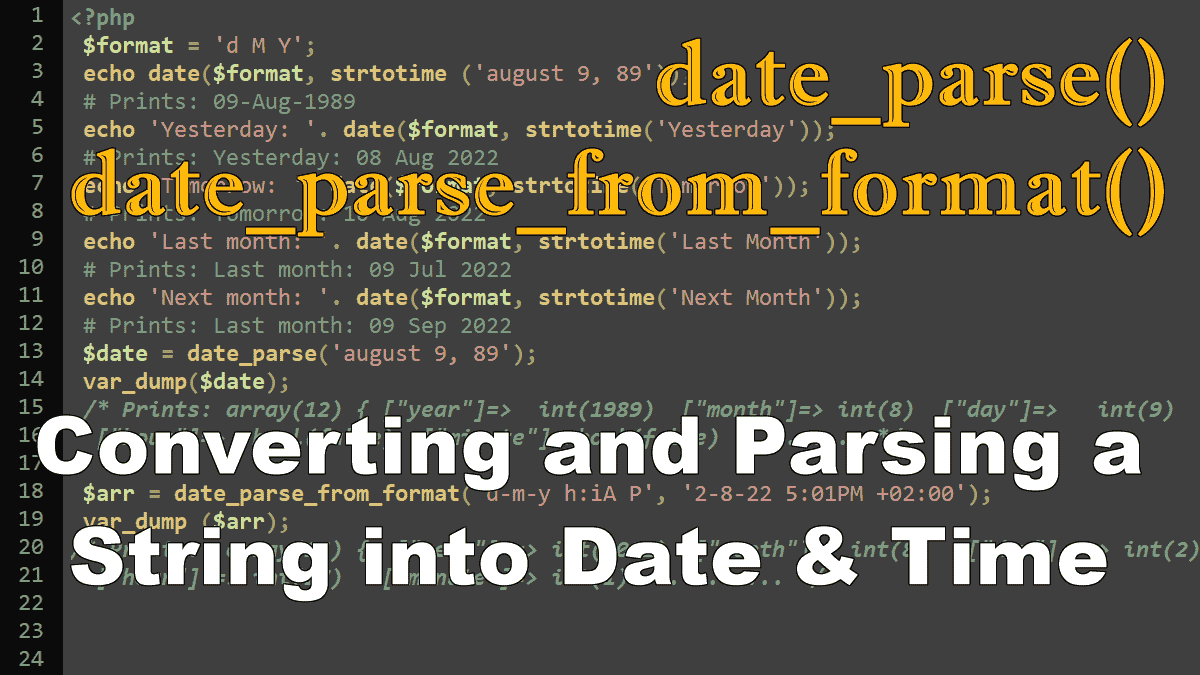
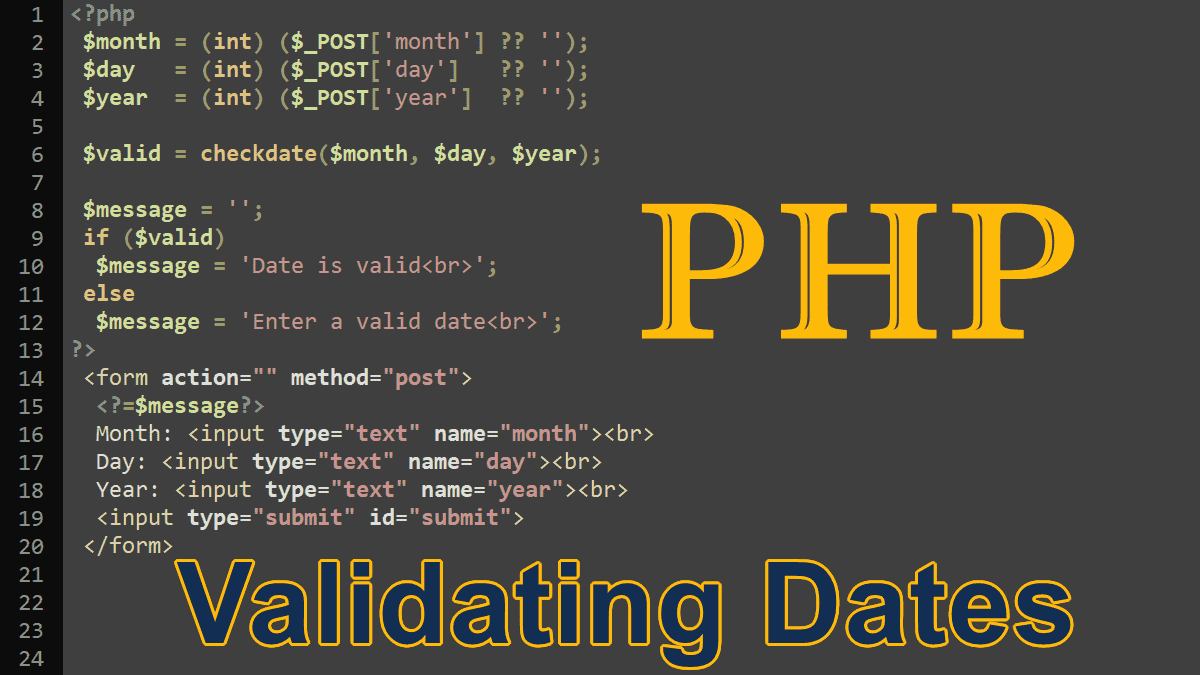
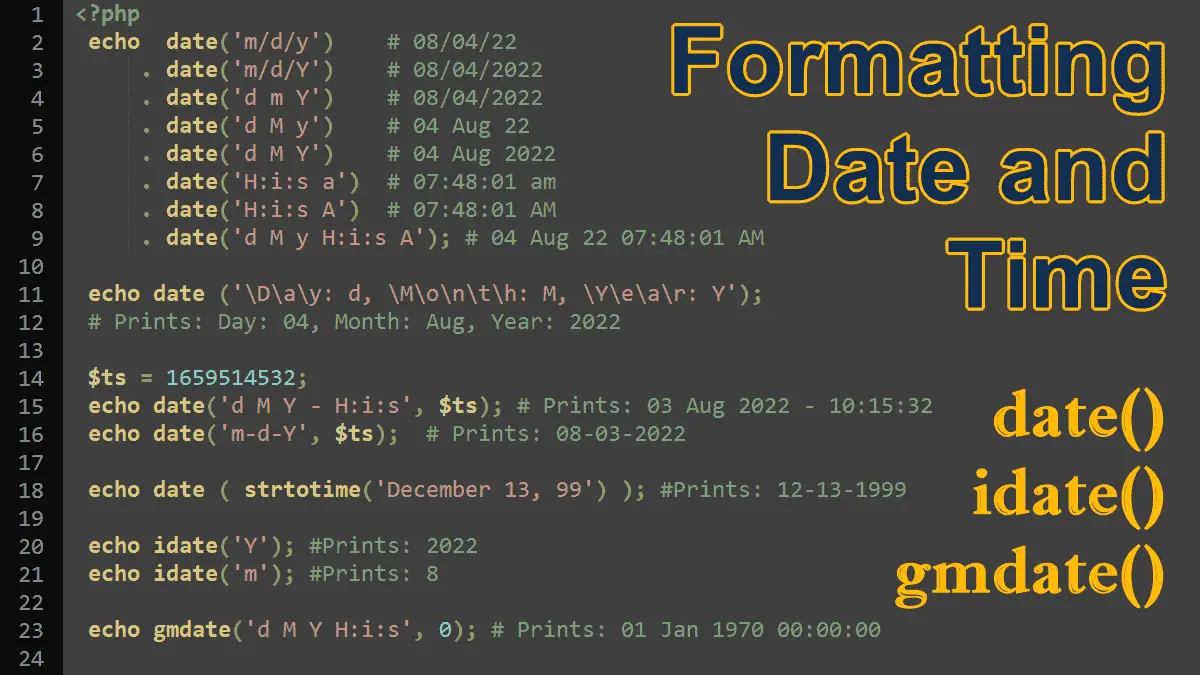
How to guess the date and time from a string with the help of strtotime() function and change the format according to your needs. You’ll also use the date_parse() and date_parse_from_format() functions which work similarly to the strtotime() function and return an associative array of date and time information.