You cannot have two classes with the same name, since PHP would not know which one is being referred to when creating a new object. To solve this issue, PHP allows the use of namespaces.
Using Namespaces


You cannot have two classes with the same name, since PHP would not know which one is being referred to when creating a new object. To solve this issue, PHP allows the use of namespaces.

A closure is an anonymous function, but an anonymous function is not a closure.

A trait defines methods and properties intended to be used by multiple classes. The structure of a trait is the same as a class, except that it’s declared using the keyword trait instead of class. You import traits into a class definition with the use keyword.

In the composition design pattern an object creates another object. Aggregation occurs when an object is composed of multiple objects.

Polymorphism is a design pattern in which classes have different functionality while sharing a common interface.
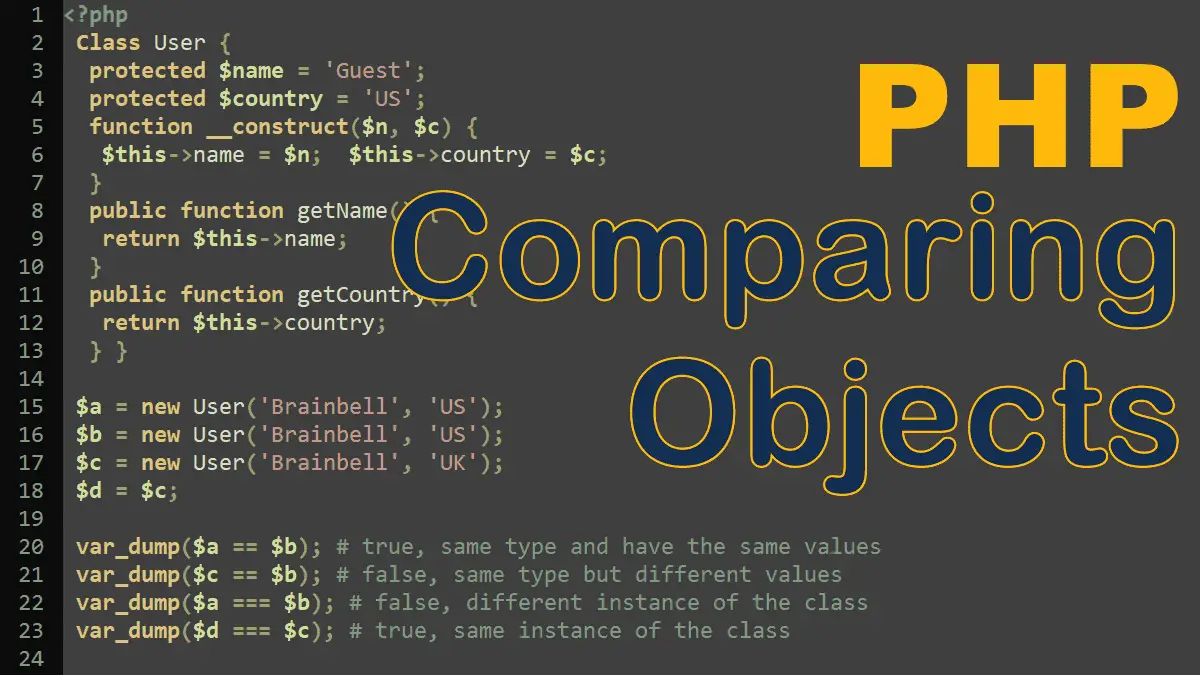
PHP provides several comparison operators that allow you to compare two values, resulting in either true or false. To compare objects, we use == and === operators.

How to use the clone keyword to clone an object and use the __clone magic method to customize the behavior of the cloning process.

In this tutorial, we explain the difference between abstract classes and interfaces.
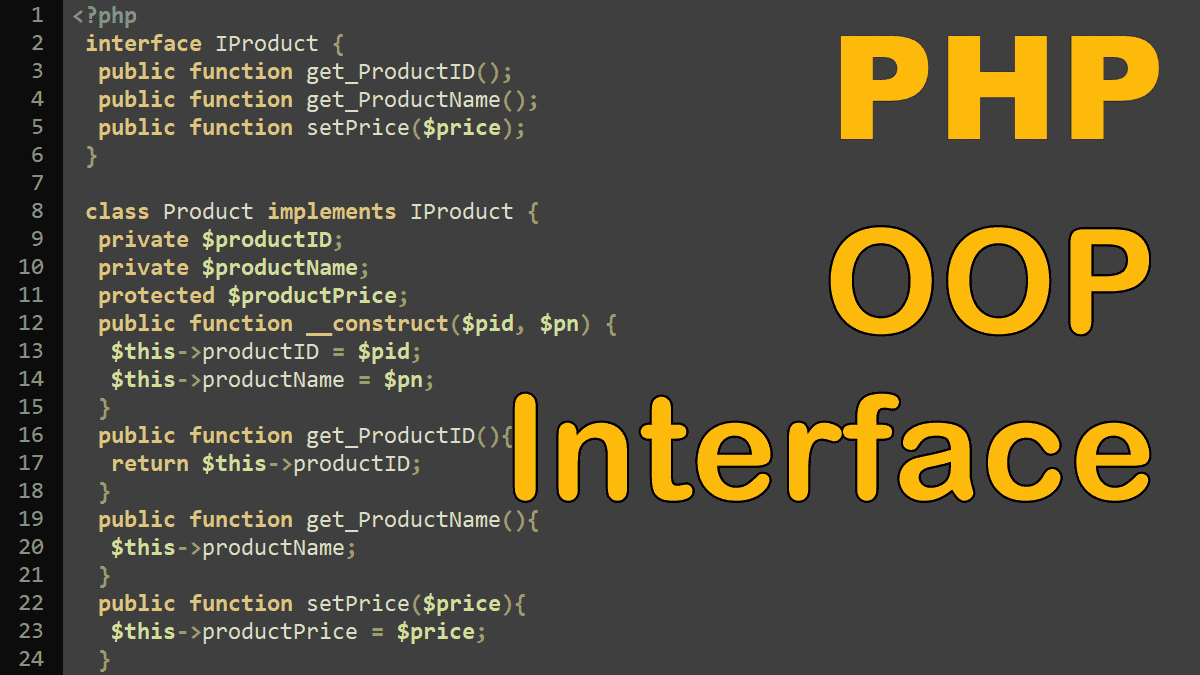
An interface is very similar to an abstract class, but it has no properties and cannot define how methods are to be implemented. Instead, it is simply a list of methods that must be implemented.

An abstract class provides a partial implementation that other classes can build upon. In addition to normal class members, it may contain incomplete methods that must be implemented in child classes.