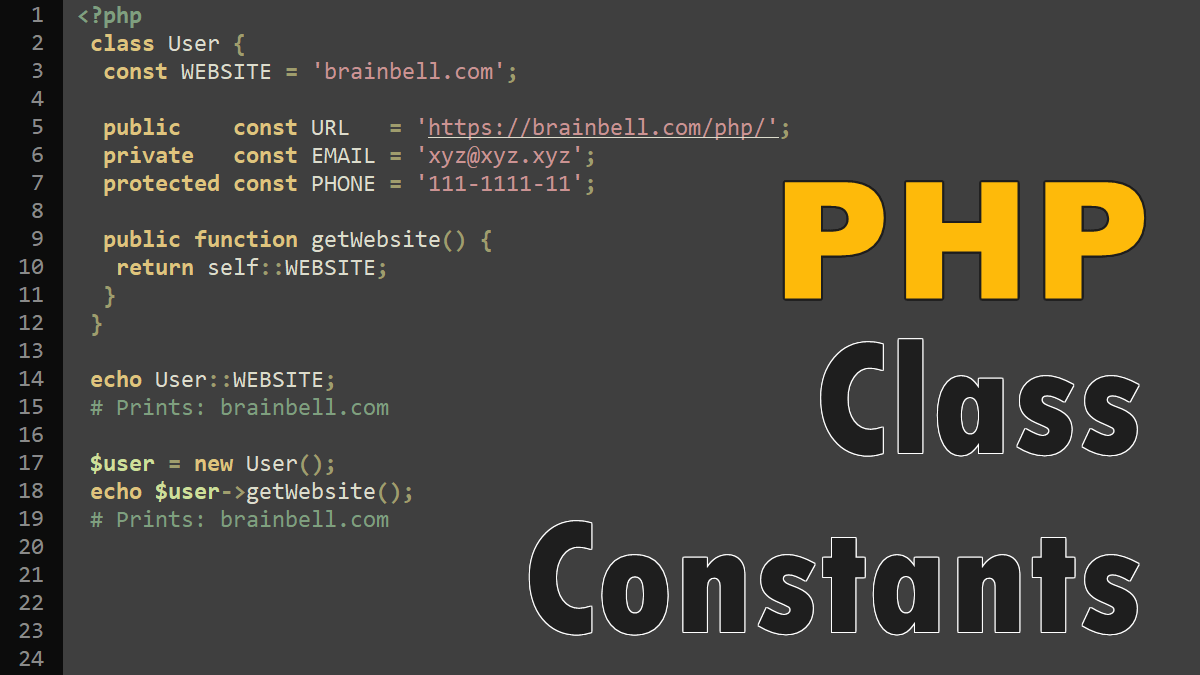
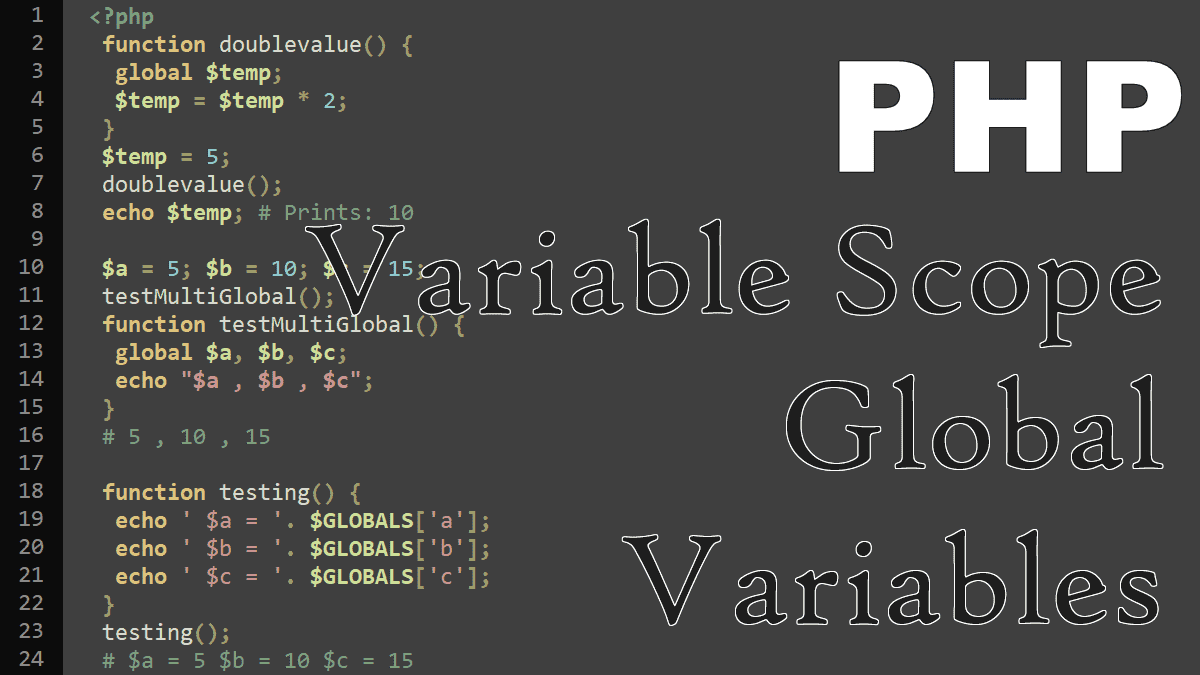
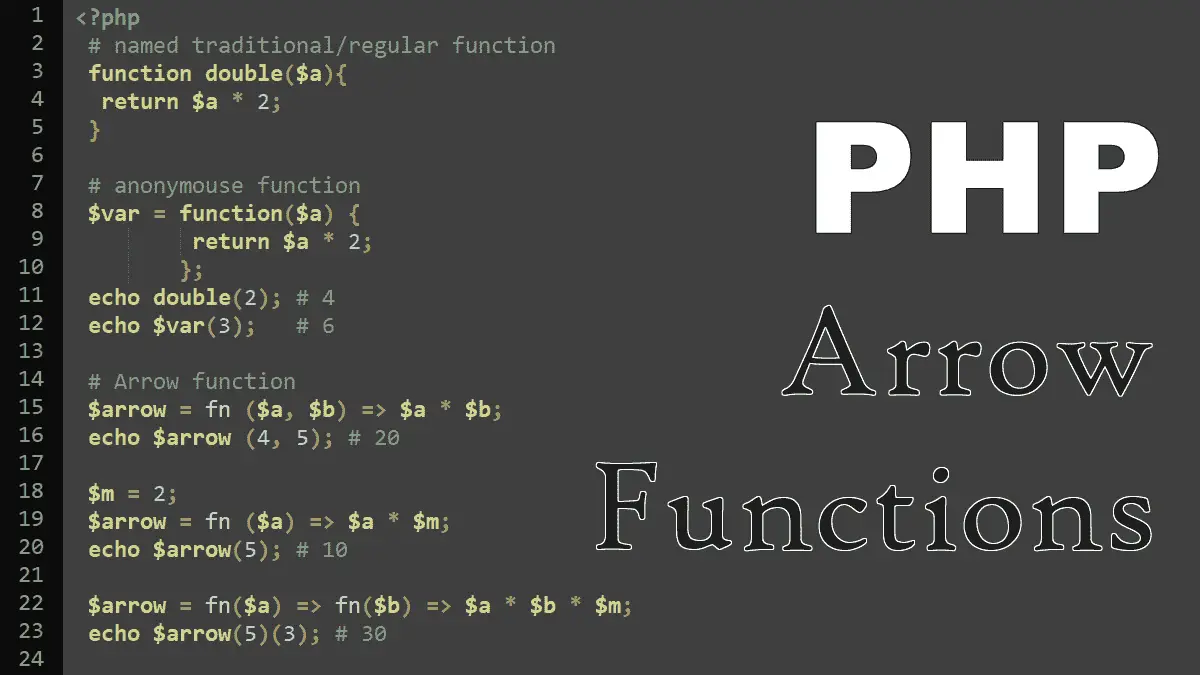
One of the powerful concepts in object-oriented programming is inheritance. Inheritance allows a new class to be defined by extending the capabilities of an existing base class. PHP allows a new class to be created by extending an existing class with the extends keyword.
OOP Inheritance