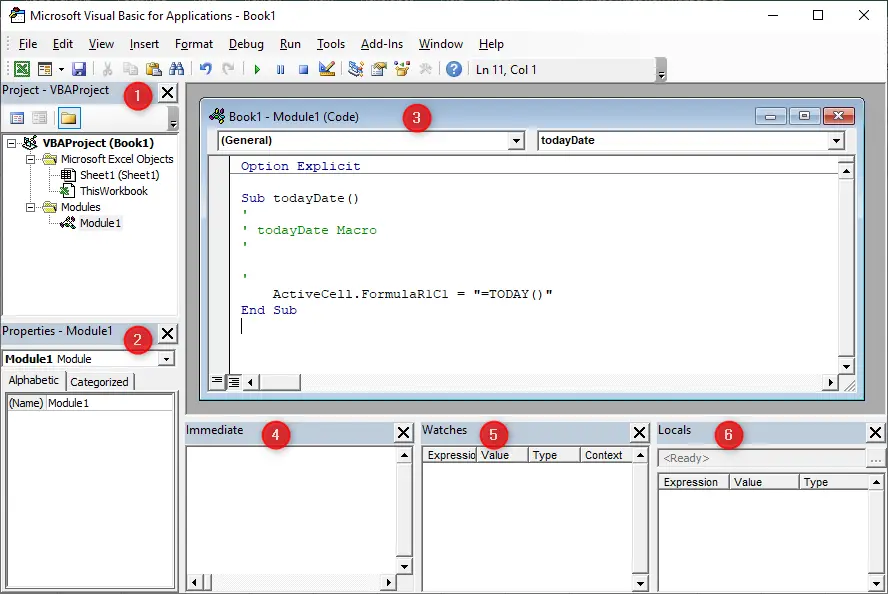
1. Project explorer
Each Excel sheet (called object in VBA) has its own code window. Double click any object on the Project Explorer tree to see its associate code window. If this window is not visible press Ctrl + R keys or click View from the top menu and then click Project Explorer.
- Microsoft Excel Objects
Sheet1 (Sheet1)
Store code for a worksheet. You’ll see multiple worksheet object if workbook contain more than one sheets (i.e. Sheet1, Sheet2, Sheet3 and so on).ThisWorkbook
Store code for the entire workbook which can access all sheets.
Modules
The Modules tree shows all independent code modules inserted on the current workbook. When the Macro Recorder created thetodayDatemacro it also created a moduleModule1in which to store the macro. To see the VBA code in that module, you can double-click the module name. ThetodayDatemacro appears in the Code window forModule1.
2. Properties window
The Properties window lists the properties for selected objects and their current settings. This list depends on what is currently selected. If this window is not visible press F4 click View > Properties Window from the menu.
3. Code window
A Code window is where you put your VBA code. Every object in a project explorer has an associated Code window. To view an object’s Code window, double-click the object in the Project explorer.
4. Immediate window
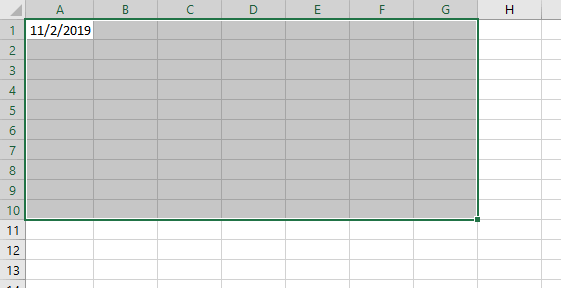
This window can be opened through the View menu or with the Ctrl + G key combination. The Immediate window is useful for issuing a VBA commands. If you type a command and press Enter, the command takes effect immediately. For example, writing range("a1","g10").select in Immediate window and pressing enter will select the range A1:G10 of the current worksheet. To see, switch back to Excel workbook, you will see that the range A1:G10 has been selected:
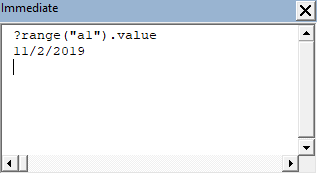
If you precede the command by a question mark, you can get an immediate answer to a question. For example, if you type ?range("a1").value, you immediately get the answer on the 2nd line:
5. Watches window
The Watch window is used for debugging. You can put a watch on one or more key variables to see how they change as the program progresses.
6. Locals
The Locals window is also used for debugging. It provides easy access to the current value of variables and objects within the scope of the function or subroutine you are running. It is an essential tool to debugging your code and stepping through changes in order to find issues.