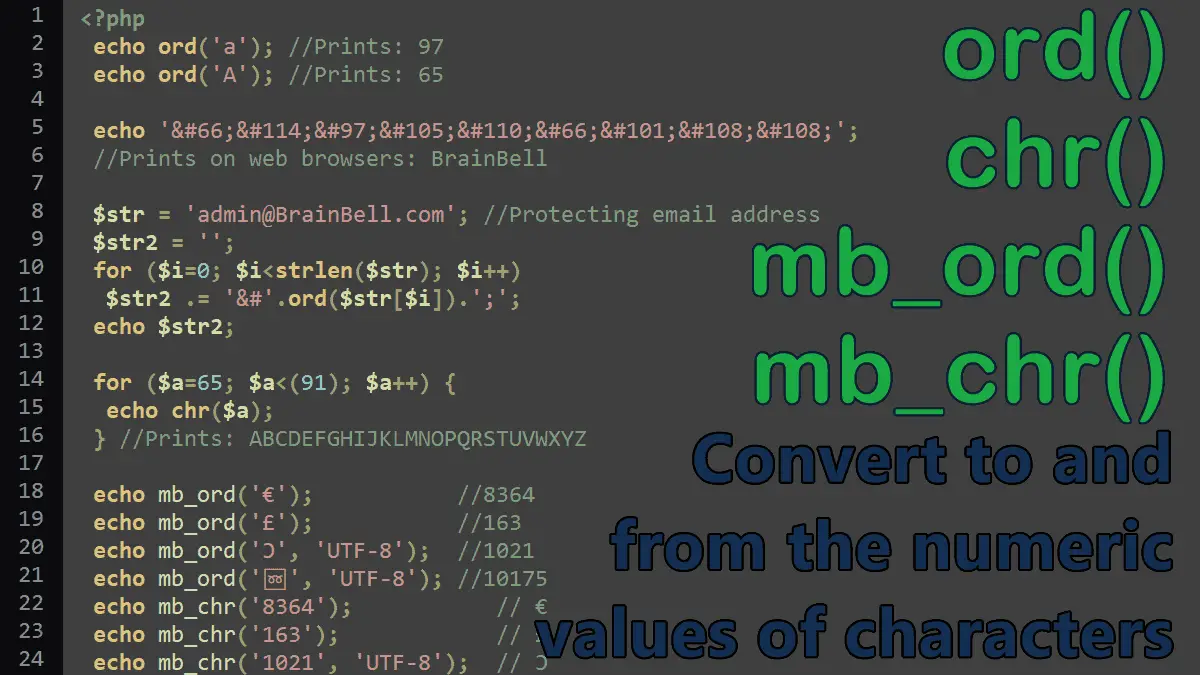
- ord()
Show ord() function result on Web Browsers
Protecting Email Address with ord() function - chr()
- mb_ord()
- mb_chr()
The ord() function
<?php //Syntax ord(string $character): int
The ord() function converts the first byte of a string to a value between 0 and 255. For example, a value is 97 and A value is 65:
<?php
echo ord('a'); //Prints: 97
echo ord('A'); //Prints: 65
This function converts the single-byte characters, use the mb_ord() function if you are dealing with multi-byte characters.
Show ord() function result on Web Browsers
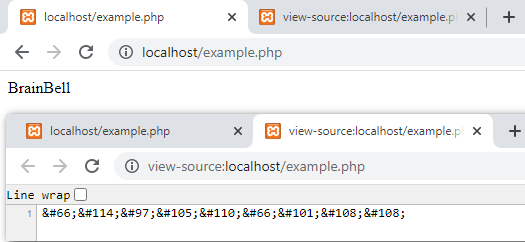
Use the HTML entities syntax and the web browser will automatically decode the number into the relevant character. For example, the ASCII value/code of B is 66, the HTML entity B displays B on a browser page, see example:
<?php echo 'BrainBell'; //Prints: BrainBell
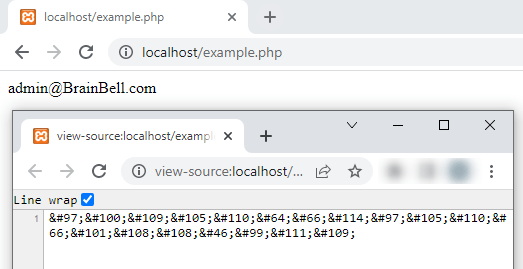
Protecting Email Address
The following code can be used to protect email addresses from spammers. Using HTML entities for email addresses, making it much harder for spam bots to find email addresses from web pages:
<?php $str = 'admin@BrainBell.com'; $str2 = ''; for ($i=0; $i<strlen($str); $i++) $str2 .= '&#'.ord($str[$i]).';'; echo $str2;
The chr() function
<?php //Syntax chr(int $codepoint): string
The chr() function does the reverse of ord() function, it generates a single-byte string from a number (0-255), use mb_chr() function if you are dealing with multi-byte characters. In the following example, we used chr() function to generate the entire alphabet:
<?php
for ($a=65; $a<(91); $a++) {
echo chr($a);
}
//ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
mb_ord()
<?php //Syntax mb_ord(string $string, ?string $encoding = null): int|false
This function has two parameters:
$string: the input string$encoding(optional): the character encoding. If null or not provided, the internal character encoding value will be used.
The mb_ord() function returns the Unicode code point value of the given character. The code point value is a numerical value that maps to a specific character.
<?php
echo mb_ord('€') . "\n";
//Prints: 8364
echo mb_ord('£') . "\n";
//Prints: 163
echo mb_ord('Ͻ', 'UTF-8') . "\n";
//Prints: 1021
echo mb_ord('ڻ', 'UTF-8') . "\n";
//Prints: 1723
echo mb_ord('➿', 'UTF-8') ."\n";
//Prints: 10175
mb_chr()
<?php //Syntax mb_chr(int $codepoint, ?string $encoding = null): string|false
This function has two parameters:
$codepoint: A Unicode codepoint value$encoding(optional): the character encoding. If null or not provided, the internal character encoding value will be used.
The mb_chr() function does the reverse of mb_ord() function, it generates a multi-byte string from a number (Unicode codepoint value), use chr() function if you are dealing with single-byte characters.
<?php
echo mb_chr('8364') . "\n";
//Prints: €
echo mb_chr('163') . "\n";
//Prints: £
echo mb_chr('1021', 'UTF-8') . "\n";
//Prints: Ͻ
echo mb_chr('1723', 'UTF-8') . "\n";
//Prints: ڻ
echo mb_chr('10175', 'UTF-8') ."\n";
//Prints: ➿
Working with Strings: