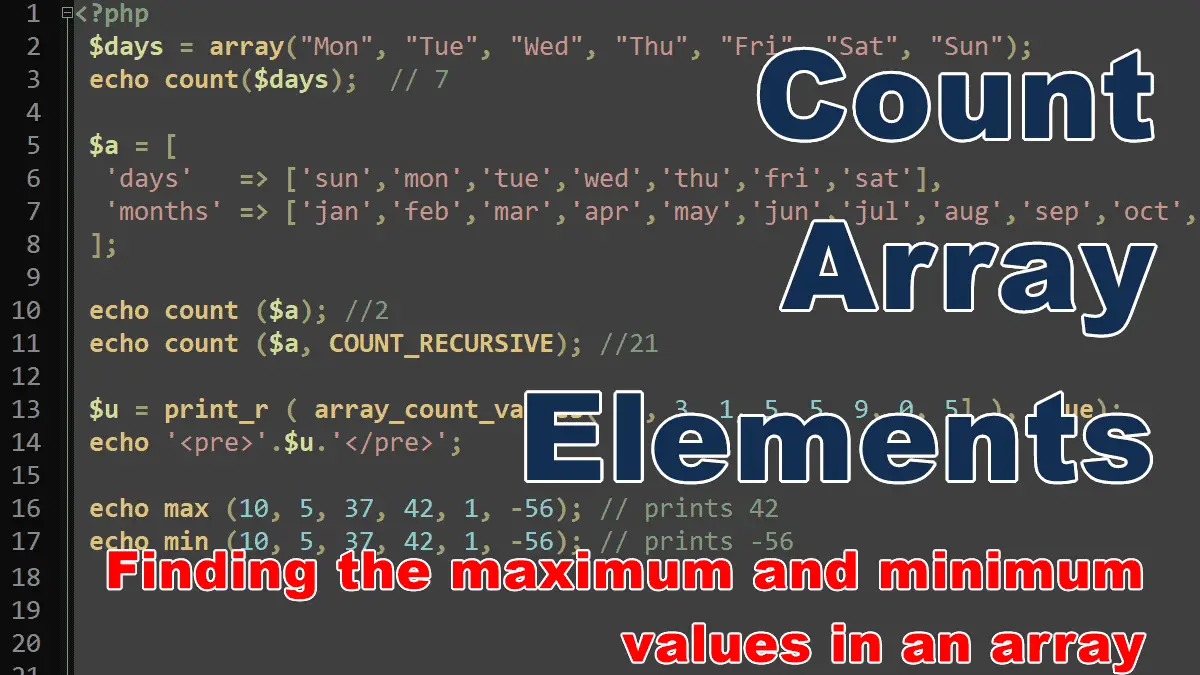
How to count elements of multidimensional or nested array, count the frequency of unique values in an array, and find the maximum and minimum values in an array.
PHP is a scripting language that’s usually embedded or combined with HTML and has many excellent libraries that provide fast, customized access to DBMSs.

How to count elements of multidimensional or nested array, count the frequency of unique values in an array, and find the maximum and minimum values in an array.

Learn how to convert arrays into strings and strings into arrays with the help of two PHP functions implode() and explode().

Along with the keys and the associated values stored in an array, PHP maintains an internal index that points to the current element in the array.

The easiest way to iterate through each element of an array is with foreach. The foreach statement lets you run a code block once for each element in an array.
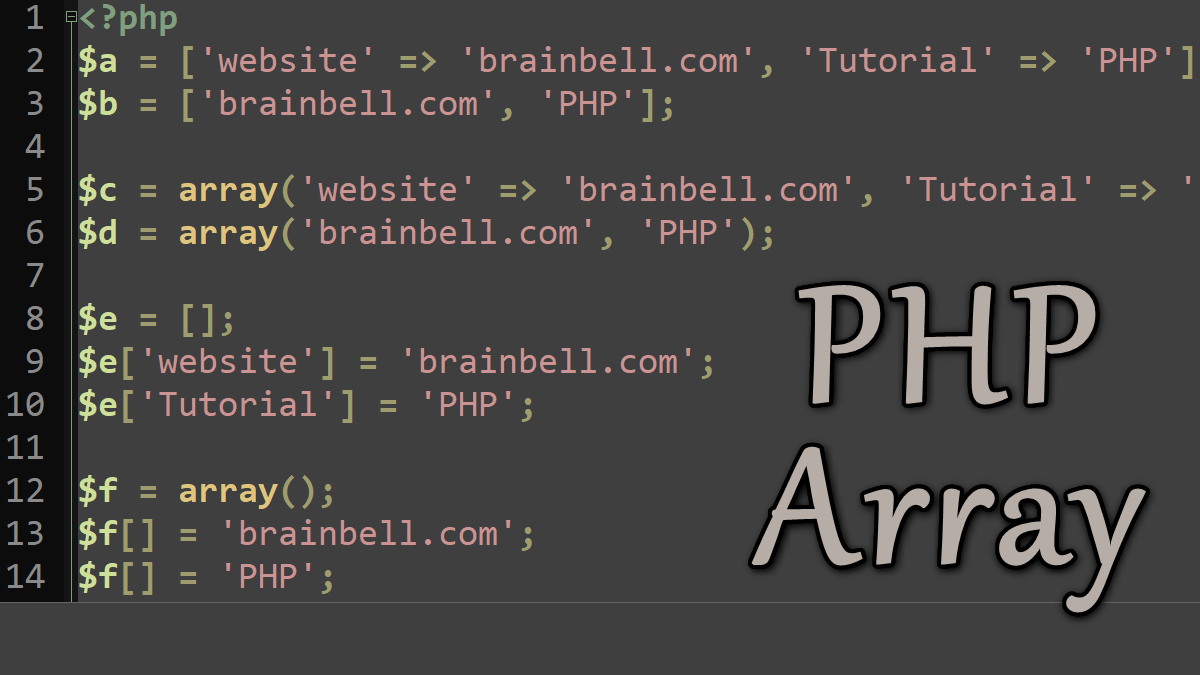
An array is an ordered set of variables, in which each variable is called an element. There are two types of arrays: numbered and associative. The first type of array uses numerical keys, whereas the latter type can also use strings as keys.

In this tutorial, you’ll create a goto operator loop. The goto operator performs a jump to a specified label (line) within the same file.

Loops add control to scripts so that statements can be repeatedly executed as long as a conditional expression remains true. There are four loop statements in PHP: while, do…while, for, and foreach. The first three are general-purpose loop constructs, and foreach is used exclusively with arrays.

In this tutorial, you’ll learn the usage of Ternary operator, ?: Elvis operator, ?? Null coalescing operator, and ??= Null coalescing assignment operator.

Comparison operators let you compare two expressions. If the comparison test is successful, the expression evaluates to true, and if the test fails, the expression evaluates to false. You often use comparison operators with conditional statements (e.g. if…else ) and loops (e.g. while loop, for loop, etc.). The logical operators work on Boolean values. You often use logical operators to combine the results of two (or more) of the comparison operators.

The control structures in PHP are similar in syntax to those in other high-level programming languages. Conditionals add control to scripts and permit branching so that different statements are executed depending on whether expressions are true or false. In this tutorial you’ll learn the two branching statements: if, with the optional else clause, and switch with two or more case clauses.