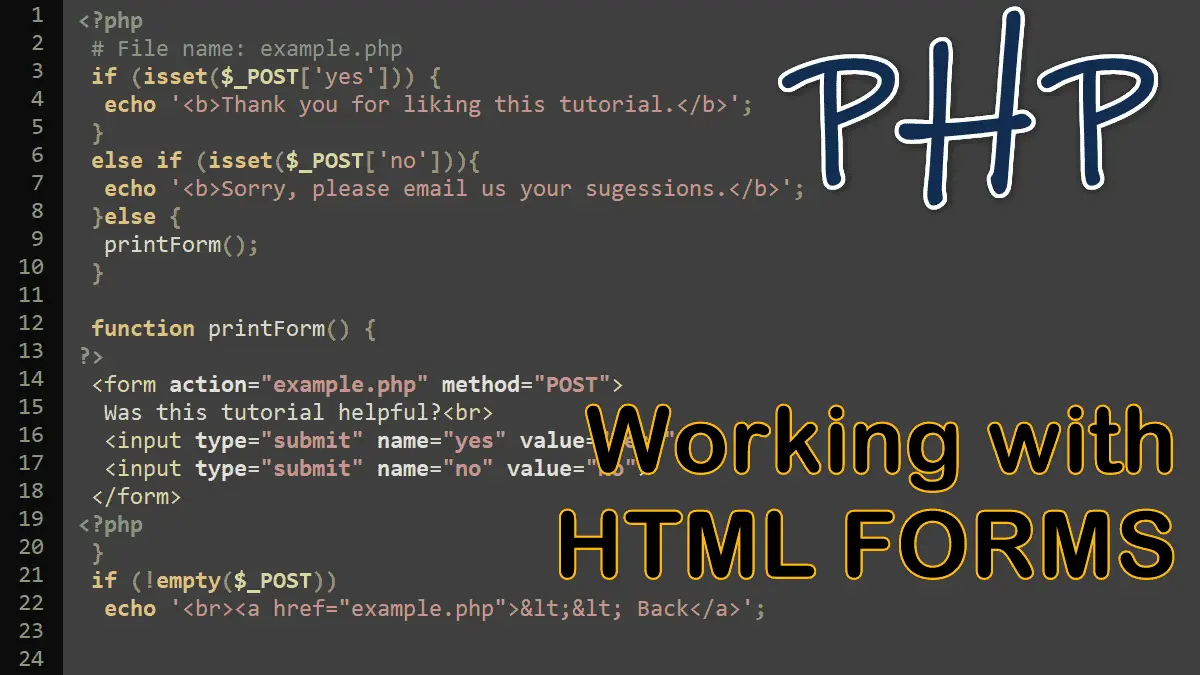
Both the GET and POST methods send data to the server, but which method should you use?
Passing Data with the HTML Forms
PHP is a scripting language that’s usually embedded or combined with HTML and has many excellent libraries that provide fast, customized access to DBMSs.

Both the GET and POST methods send data to the server, but which method should you use?

In this tutorial, we discuss how to pass user data from a web browser to a PHP script. You will see how HTTP requests can include user data by creating URLs and embedding links in HTML documents.
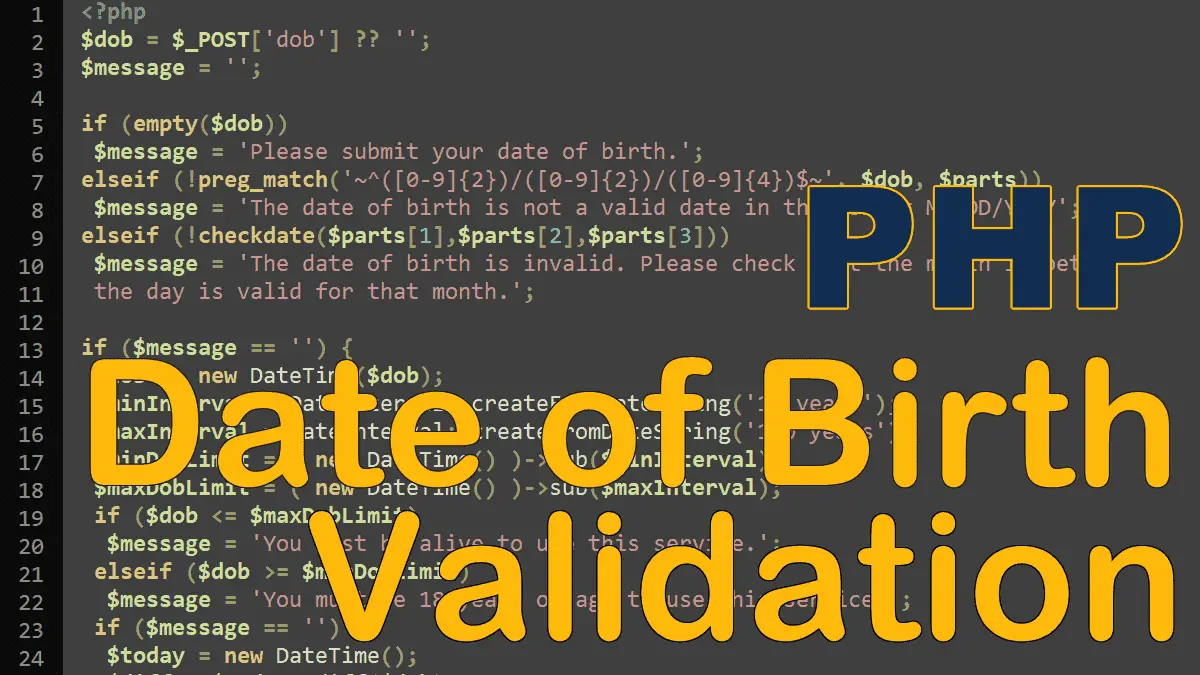
Dates of birth are commonly entered by users. Most dates require checks to see if the date is valid and also if it’s in a required range. In this tutorial, we’ll create a PHP script that validates the given date of birth to check whether it’s in a valid range.

The PHP autoloading feature allows you to load class files automatically in your program. PHP calls an autoloader function when you reference a class, and the autoloader function tries to figure out which file that class is in.

You cannot have two classes with the same name, since PHP would not know which one is being referred to when creating a new object. To solve this issue, PHP allows the use of namespaces.

A closure is an anonymous function, but an anonymous function is not a closure.

A trait defines methods and properties intended to be used by multiple classes. The structure of a trait is the same as a class, except that it’s declared using the keyword trait instead of class. You import traits into a class definition with the use keyword.

In the composition design pattern an object creates another object. Aggregation occurs when an object is composed of multiple objects.

Polymorphism is a design pattern in which classes have different functionality while sharing a common interface.
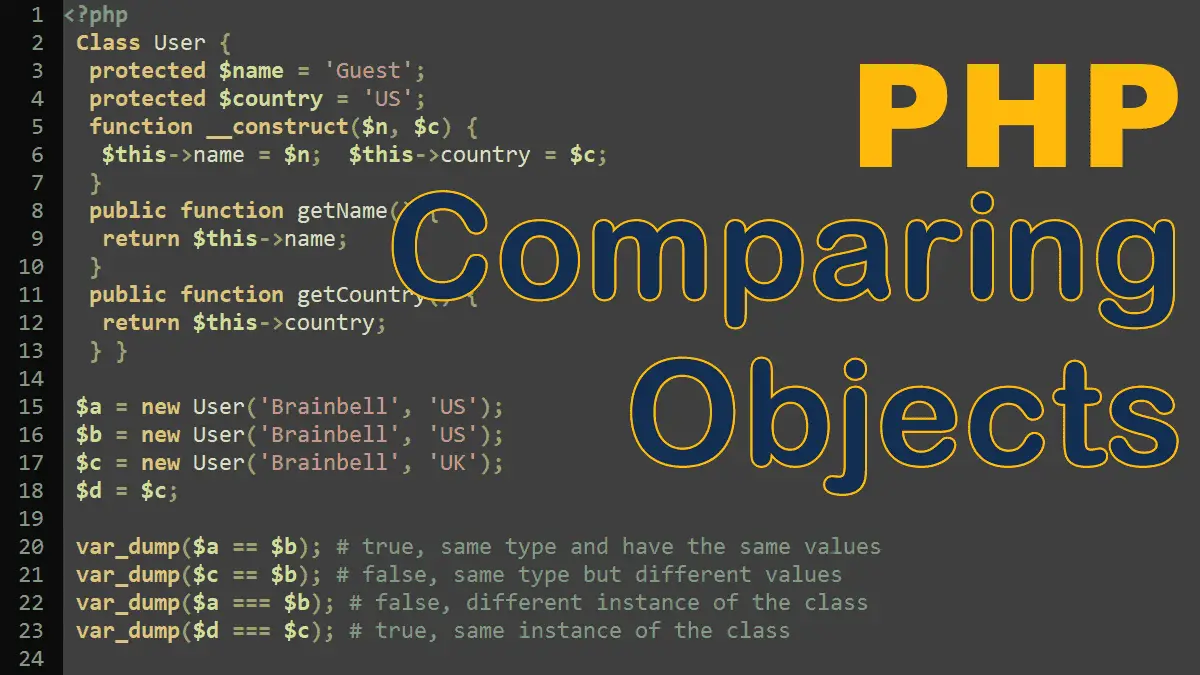
PHP provides several comparison operators that allow you to compare two values, resulting in either true or false. To compare objects, we use == and === operators.