- Calculate Total Hours
- Calculate Total Minutes
- Calculate Total Seconds
- Number to Time or Vice Versa
- Difference Between Two Times
- Add Seconds, Minutes, or Hours to a Time
- Difference Between Two Dates
- Add Days, Months, or Years to a Date
Calculate Total Hours
You can add times by using the SUM function (or a simple plus sign). Therefore, =SUM(A1:A5) would result in Total Hours if A1:A5 contained valid times. See the following figure:
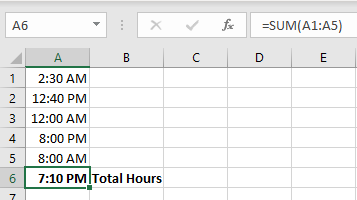
There is, however, a big “Gotcha!” Unless told otherwise, Excel will not add past 24 hours. This is because when a time value exceeds 24 hours (a true value of 1), it rolls into a new day and starts again.
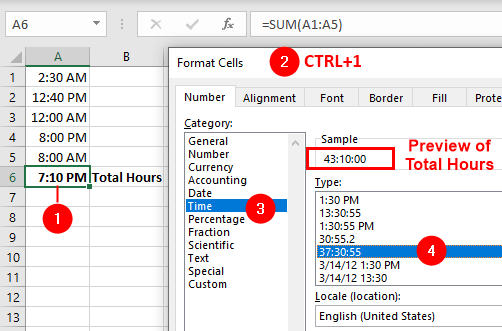
To force Excel not to default back to a new day after 24 hours, you can use a cell format of 37:30:55 or a custom format of [h]:mm:ss, see the following figure:
Calculate Total Minutes
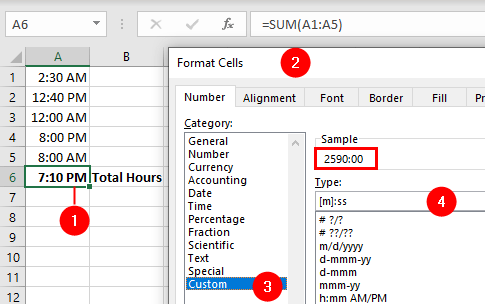
You can use a similar format to get the total minutes or seconds of a time. To get the total minutes of the time 24:00, for instance, format the cell as [m] and you will get 1440.
Calculate Total Seconds
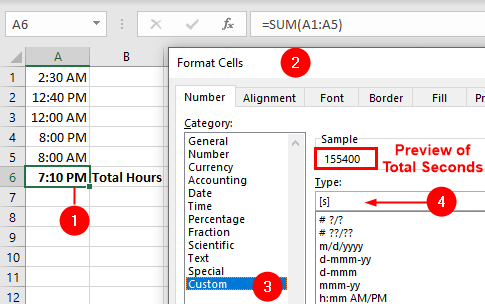
To get the total seconds, use a custom format of [s] and you get 86400.
Number to Time or Vice Versa
If you want to use these real-time values in other calculations, keep the following “magic” numbers in mind:
1 Minute = 60 Seconds
1 Hour = 60 Minutes = 3600 Seconds
1 Day = 24 Hours = 1440 Minutes = 86400 Seconds| 1 Minute | = | 60 seconds |
| 1 Hour | = | 60 minutes or 3600 seconds (60 seconds X 60 minutes) |
| 1 Day | = | 24 hours or 1440 minutes (24 hours X 60 minutes) or 86400 seconds (24 hours X 60 minutes X 60 seconds) |
Once you are armed with these magic numbers and the preceding information, you’ll find it’s much easier to manipulate times and dates. Take a look at the following examples to see what we mean (assume the time is in cell A1).
If you have the number 5.50 and you really want 5:30 or 5:30 a.m., use this: =A1/24 and format as needed:
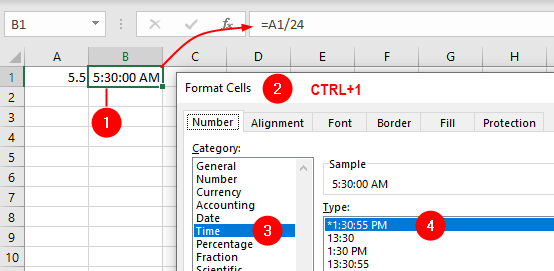
If it should be 17:30 or 5:30 p.m., use this: =(A1/24)+0.5:
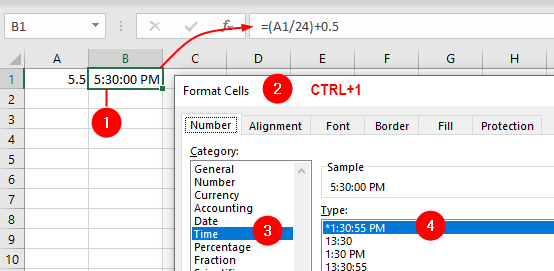
To achieve the opposite, that is, a decimal time from a true time, use this: =A1*24:
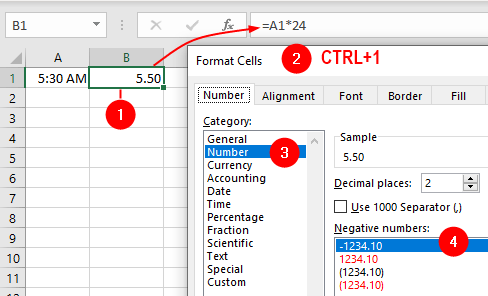
If a cell contains the true date and the true time (as in 18/Aug/23 15:36) and you want only the date, use this: =INT(A1):
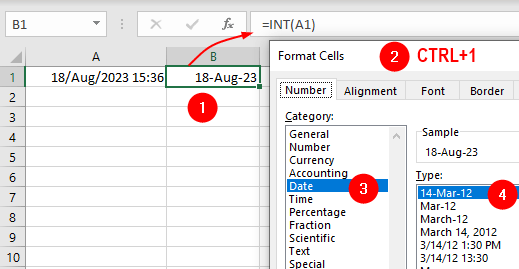
To get only the time, use this: =A1-INT(A1) or: =MOD(A1,1) and format as needed:
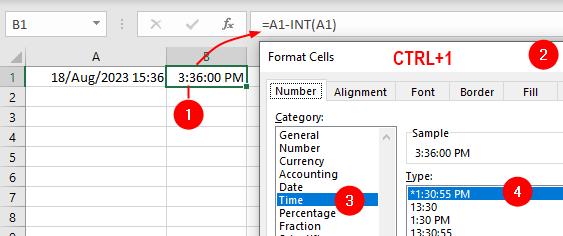
Difference Between Two Times
To calculate the difference between two times in Excel, you can use the subtraction operator - directly on the time values, you can use the TEXT function to format the difference. Here’s how you can do it using both methods:
For example, you might need to account for start time and end time, with the start time being 8:50 p.m. in cell A1, and the end time being 9:50 a.m. in cell A2. If you subtract the start time from the end time (=A1-A2), you get ######, as Excel, by default, cannot work with negative times.
See Display Negative Time Value for more on how to work with negative times.
Alternatively, you can work around this in the following way, ensuring a positive result:
=MAX(A1:A2)-MIN(A1:A2)TEXT Function: Find out the difference between two time
Enter the starting time in A1 and the ending time in A2. In a third cell A3, enter the formula:
=TEXT(A2-A1, "h:m:s")This formula uses the TEXT function to format the difference in hours, minutes, and seconds between the two times.
Add Seconds, Minutes, or Hours to a Time
You can also tell Excel to add any number of seconds, minutes, or hours to any time:
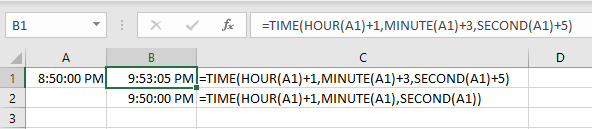
=TIME(HOUR(A1)+value1,MINUTE(A1)+value2,SECOND(A1)+value3)To add one minute to a time in cell A1, use this:
=TIME(HOUR(A1),MINUTE(A1)+1,SECOND(A1))To add one hour, three minutes, and five seconds to a time in cell A1, use this:
=TIME(HOUR(A1)+1,MINUTE(A1)+3,SECOND(A1)+5)Difference Between Two Dates
To calculate the difference between two dates in Excel, you can use simple subtraction or the DATEDIF function. To find out the difference between two dates, use this simple subtraction:
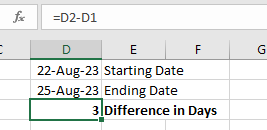
- Enter the starting date in cell
D1and the ending date in cellD2. - In the cell
D3, enter the formula:=D2 - D1. - The result in cell
D3will be the difference between the two dates in days.
To find out the difference between two dates with the DATEDIF function:
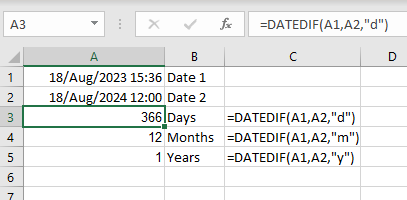
Use this: =DATEDIF(A1,A2,"d") where D1 is the earlier date. This will produce the number of days between the two dates. It also will accept “m” or “y” as the result to return, i.e., Months or Years:
If you do not know in advance which date or time is the earliest, the MIN and MAX functions can help. For example, to be assured of a meaningful result, you can use this:
=DATEDIF(MIN(A1,A2),MAX(A1,A2),"d")Add Days, Months, or Years to a Date
You can also tell Excel to add any number of days, months, or years to any date:
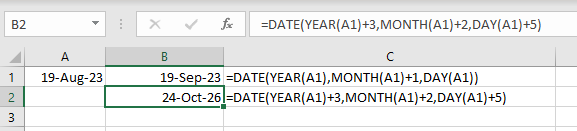
Syntax:
=DATE(YEAR(A1)+value1,MONTH(A1)+value2,DAY(A1)+value3)To add one month to a date in cell A1, use this:
=DATE(YEAR(A1),MONTH(A1)+1,DAY(A1))To add three years, two months, and five days in cell A1, use this:
=DATE(YEAR(A1)+3,MONTH(A1)+2,DAY(A1)+5)Date and Time
- How Date and Time Feature Works in Excel
- Calculate Date and Time
- Display Negative Time Values
- Count All Occurrence of a Specific Day in a Month or Two Dates
- Calculate Working Days and Holidays
- Determine Deadlines, Schedules, or Due Dates
- Show Total Time as Days, Hours, and Minutes
- Format Date and Time Values
