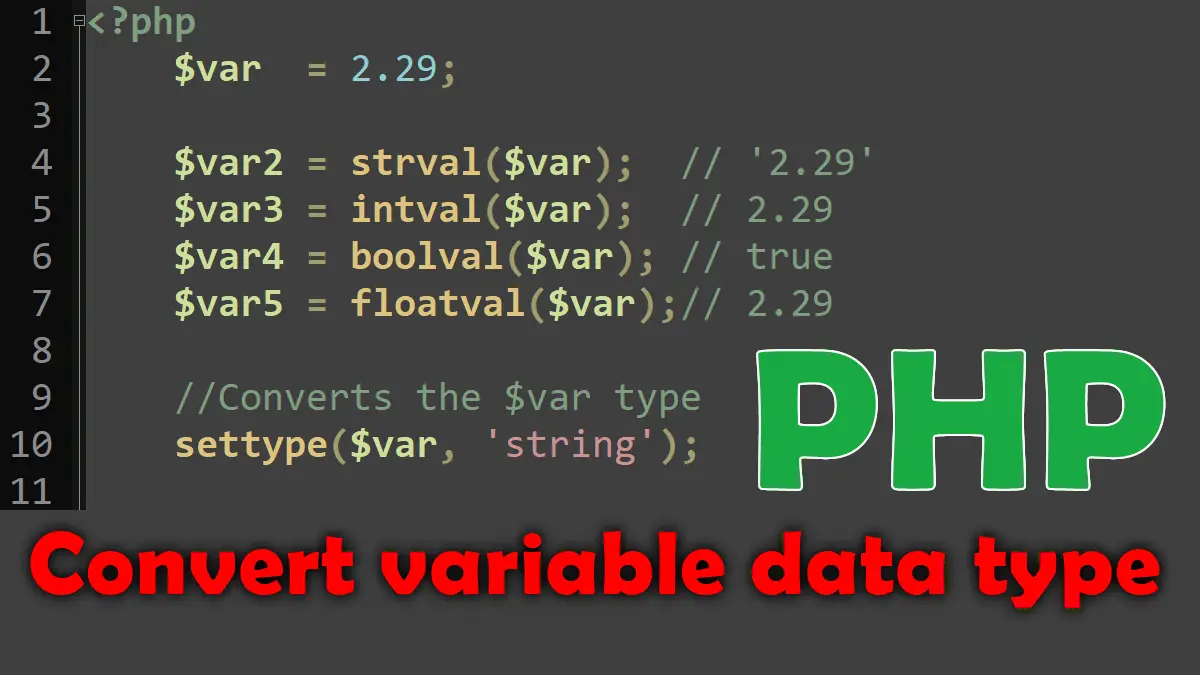
<?php $var = 2.29; $var2 = strval($var); // '2.29' $var3 = intval($var); // 2.29 $var4 = boolval($var); // true $var5 = floatval($var);// 2.29 //Converts the $var type settype($var, 'string');
This tutorial covers the following topics:
- settype
- strval
- boolval
- intval
- floatval
- Type casting
- Automatic Type Conversion
- Implicit vs Explicit Casting
settype() – Change Variable’s Data Type
The function settype($var, "type") can explicitly set the type of variable to type, where type is again one of array, boolean, float, integer, object, null or string. To use settype($var, 'type'), pass in the name of the variable you want to alter, followed by the type to change the variable to (in quotation marks).
Here’s some example code that converts a variable to various different types using settype:
$var = 2.23; echo $var; // Displays "2.23" echo gettype($var); //prints double settype( $var, "string" ); echo $var; // Displays "2.23" echo gettype($var); //prints string settype( $var, "integer" ); echo $var; // Displays "2" echo gettype($var); //prints integer settype( $var, "float" ); echo $var; // Displays "2" echo gettype($var); //prints double settype( $var, "boolean" ); echo $var; // Displays "1" echo gettype($var); //prints boolean settype( $var, "null" ); echo $var; // Displays nothing echo gettype($var); //prints NULL
To start with, the $var variable contains 2.23 , a floating-point value. Next, $var is converted to a string, which means that the number 2.23 is now stored using the characters 2, . (period), 2 , and 3. After converting $var to an integer type, it contains the value 2 ; in other words, the fractional part of the number has been lost permanently.
You can see this in the next two lines, which convert $var back to a float and display its contents. Even though $var is a floating-point variable again, it now contains the whole number 2 . After converting $var to a Boolean, it contains the value true (which PHP displays as 1 ). This is because PHP converts a non-zero number to the Boolean value true.
strval($var)
The strval function is used to convert any scalar value (integer, boolean or float (or double)) to a string. If we use it with a composite type (array, object) then this function only returns the “type name” of the value being converted.
Example: Converting float (or double) to string
//Converting float type to string $var = 3.23; $var2 = strval($var); echo gettype($var2); // string
Example: Converting Boolean to string
//Converting true to string $var = true; $var2 = strval($var); echo $var2; // prints 1 echo gettype($var2); // string //Converting false to string $var = false; $var2 = strval($var); echo $var2; // prints nothing (empty string) echo gettype($var2); // string
Example: Converting array to string
$arr = [1,2,3]; $str = strval($arr); // will not convert //Prints the type of variable echo $arr; // Array echo $str; // Array
boolval($var)
The boolval() function gives the Boolean value for a given variable.
Example: Converting string to Boolean
$str = 'BrainBell'; $bol = boolval($str); // prints 1 (for true) echo $bol; echo gettype($bol); // boolean
Example: Converging empty string to Boolean
$str = ''; $bol = boolval($str); // prints nothing (for false) echo $bol; echo gettype($bol); // boolean
Example: Converting integer to Boolean
$int = 1; $bol = boolval($int); // prints 1 (for true) echo $bol; echo gettype($bol); // boolean
Example: Converting zero (0) to Boolean
$int = 0; $bol = boolval($int); // prints nothing (for false) echo $bol; echo gettype($bol); // boolean
intval($var, $base)
This function returns the integer value of a variable.
Example: Converting string to integer
$str = "BrainBell"; $int = intval($str); echo $int; // 0 echo gettype($int); // integer
Example: Converting numeric string to integer
$str = "123 BrainBell 456 .com 100"; $int = intval($str); echo $int; // 123 echo gettype($int); // integer
Example: Converting Boolean to integer
//Converting true $bol = true; $int = intval($bol); echo $int; // 1 echo gettype($int); // integer //Converting false $bol = false; $int = intval($bol); echo $int; // 0 echo gettype($int); // integer
Converting non-decimal number to decimal
intval() function has another use: converting from a non-decimal(non-base-10) integer to a base-10 (decimal) integer. To use this feature, pass intval() a string representation of the non– base-10 integer, followed by the base of the integer. For example, intval("1011" , 2) returns a value of 11 (the base-2 number 1011 converted to a decimal number).
Example: Converting binary string to decimal integer
$bin = "1011"; $int = intval ($bin, 2); echo $int; // 11
Example: Converting binary number to decimal
//The binary 1011 $bin = 0b1011; $int = intval ($bin, 2); echo $int; // 11
Note: As of PHP 5.4 the prefix for binary number (base-2) is: 0b (as shown in above example).
Example: Converting octal number to decimal
//The octal 13 $oct = 013; $int = intval ($oct, 8); echo $int; // 11
Note: Prefix for octal number (base-8) is: 0 (as shown in above example).
Example: Converting hexadecimal number to decimal
//The hexadecimal 45b $hex = 0x45b; $int = intval ($hex, 8); echo $int; // 1115
Note: Prefix for hexadecimal number (base-16) is: 0x (as shown in above example).
floatval($str)
This function returns the float value of a variable.
Example: Convert string to float
$str = "BrainBell"; $flt = floatval($str); echo $flt; // 0 echo gettype($flt); // double
Example: Convert numeric string to float
$str = "2.2 BrainBell"; $flt = floatval($str); echo $flt; // 2.2 echo gettype($flt); // double
Example: Convert Boolean to float
//Converting true $bol = true; $flt = floatval($bol); echo $flt; // 1 echo gettype($flt); // double //Converting false $bol = false; $flt = floatval($bol); echo $flt; // 0 echo gettype($flt); // double
Type casting
PHP supports type-casting in much the same way as C, to allow the type of an expression to be changed. By placing the type name in parentheses in front of a variable, PHP converts the value to the desired type:
- Cast to integer
(int) $varor(integer) $var - Cast to Boolean
(bool) $varor(boolean) $var - Cast to float
(float) $var,(double) $varor(real) $var - Cast to string
(string) $var - Cast to array
(array) $var - Cast to object
(object) $var
The rules for converting types are mostly common sense, but some conversions may not appear so straightforward. Following examples show how various values of $var are converted using the (int), (bool), (string), and (float) casting operators.
Type conversion with casting operators
We’ll use var_dump function to display variable’s information. This function displays structured information about one or more expressions that includes its type and value.
Casting null to int, bool, string and float
$var = null; var_dump( (int) $var, // 0 (bool) $var, // false (string) $var,// "" empty string (float) $var // 0 ); /*Results int(0) bool(false) string(0) "" float(0) */
Casting true to int, bool, string and float
$var = true; var_dump( (int) $var, // 1 (bool) $var, // true (string) $var, // "1" (float) $var // 1 ); /*Results int(1) bool(true) string(1) "1" float(1) */
Casting false to int, bool, string and float
$var = false; var_dump( (int) $var, // 0 (bool) $var, // false (string) $var, // "" empty string (float) $var // 0 ); /*Results int(0) bool(false) string(0) "" float(0) */
Casting 0 to int, bool, string and float
$var = 0; var_dump( (int) $var, // 0 (bool) $var, // false (string) $var, // 0 (float) $var // 0 ); /*Results int(0) bool(false) string(1) "0" float(0) */
Casting 7.3 to int, bool, string and float
$var = 7.3; var_dump( (int) $var, // 7 (bool) $var, // true (string) $var, // "7.3" (float) $var // 7.3 ); /* Results int(7) bool(true) string(3) "7.3" float(7.3) */
Casting "0" to int, bool, string and float
$var = "0"; var_dump( (int) $var, // 0 (bool) $var, // false (string) $var, // "0" (float) $var // 0 ); /* Results int(0) bool(false) string(1) "0" float(0) */
Casting "18" to int, bool, string and float
$var = "18"; var_dump( (int) $var, // 18 (bool) $var, // true (string) $var, // "18" (float) $var // 18 ); /* Results int(18) bool(true) string(2) "18" float(18) */
Casting "1968 to present" to int, bool, string and float
$var = "1968 to present"; var_dump( (int) $var, // 1968 (bool) $var, // true (string) $var, // "1968 to present" (float) $var // 1968 ); /* Results int(1968) bool(true) string(15) "1968 to present" float(1968) */
Casting "hello" to int, bool, string and float
$var = "hello"; var_dump( (int) $var, // 0 (bool) $var, // true (string) $var, // "hello" (float) $var // 0 ); /* Results int(0) bool(true) string(5) "hello" float(0) */
Table showing the values and results of all above examples:
| Value of $var | (int) $var | (bool) $var | (string) $var | (float) $var |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| null | 0 | false | “” | 0 |
| true | 1 | true | “1” | 1 |
| false | 0 | false | “” | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | false | “0” | 0 |
| 7.3 | 7 | true | “7.3” | 7.3 |
| “0” | 0 | false | “0” | 0 |
| “18” | 18 | true | “18” | 18 |
| “1968 to present” | 1968 | true | “1968 to present” | 1968 |
| “hello” | 0 | true | “hello” | 0 |
Automatic type conversion
Automatic type conversion occurs when two differently typed variables are combined in an expression or when a variable is passed as an argument to a library function that expects a different type. When a variable of one type is used as if it were another type, PHP automatically converts the variable to a value of the required type. The same rules are used for automatic type conversion as are demonstrated in previous page Table.
Some simple examples show what happens when strings are added to integers and floats and when strings and integers are concatenated:
// $var is set as an integer = 25 $var = "10" + 15; // $var is set as a float = 25.0 $var = "10" + 15.0; // $var is set as a string = "15 Steps" $var = 15 . " Steps";
Not all type conversions are so obvious and can be the cause of hard-to-find bugs:
// $var is set as an integer = 15 $var = 15 + " Steps"; // $var is an integer = 17 $var = 15 + "2 blind mice"; // $var is a float, but what does it mean $var = "test" * 5 + 4.14159;
Automatic type conversion can change the type of a variable. Consider the following example:
$var = "1"; // $var is a string == "1" $var += 2; // $var is now an integer == 3 $var /= 2; // $var is now a float == 1.5 $var *= 2; // $var is still a float == 3
Care must be taken when interpreting non-Boolean values as Boolean. Many library functions in PHP return values of different types: false if a valid result could not be determined, or a valid result. A valid return value of 0, 0.0, "0", an empty string, null, or an empty array is interpreted false when used as a Boolean value.
Implicit vs Explicit Casting
PHP is a loosely typed language that allows you to declare a variable and its type simply by using it. It also automatically converts values from one type to another whenever required. This is called implicit casting.
Converting the type of a variable using a function is called explicit casting, for example:
$str = "12 is a string"; // integer $num1 = (int) $str; // or $num2 = intval($str); echo $num1; //12 echo $num2; //12
Data types in PHP: