Listing 10.1. The Contacts Example XML Document
1: <?xml version="1.0"?> 2: <?xml-stylesheet type="text/css" href="contacts.css"?> 3: <!DOCTYPE contacts SYSTEM "contacts.dtd"> 4: 5: <contacts> 6: <! This is my good friend Frank. > 7: <contact> 8: <name>Frank Rizzo</name> 9: <address>1212 W 304th Street</address> 10: <city>New York</city> 11: <state>New York</state> 12: <zip>10011</zip> 13: <phone> 14: <voice>212-555-1212</voice> 15: <fax>212-555-1342</fax> 16: <mobile>212-555-1115</mobile> 17: </phone> 18: <email>frank.rizzo@franksratchetco.com</email> 19: <company>Frank's Ratchet Service</company> 20: <notes>I owe Frank 50 dollars.</notes> 21: </contact> 22: 23: <! This is my old college roommate Sol. > 24: <contact> 25: <name>Sol Rosenberg</name> 26: <address>1162 E 412th Street</address> 27: <city>New York</city> 28: <state>New York</state> 29: <zip>10011</zip> 30: <phone> 31: <voice>212-555-1818</voice> 32: <fax>212-555-1828</fax> 33: <mobile>212-555-1521</mobile> 34: </phone> 35: <email>srosenberg@rosenbergshoesglasses.com</email> 36: <company>Rosenberg's Shoes & Glasses</company> 37: <notes>Sol collects Civil War artifacts.</notes> 38: </contact> 39: </contacts>
Notice in the code for the Contacts document that an external style sheet (contacts.css) is associated with the document through the xml-stylesheet processing instruction (line 2). Beyond that, there is nothing specific to style sheets in the XML code. However, it's important to understand the role of a style sheet in this example, which is to display the mailing address for each contact. Knowing this, it is necessary to hide the phone number and company name when formatting the content for display. This is accomplished in the contacts.css style sheet, which is shown in Listing 10.2.
Listing 10.2. The contacts.css Style Sheet Used to Format the Contacts XML Document
1: contact {
2: display:block;
3: width:350px;
4: padding:5px;
5: margin-bottom:10px;
6: border:5px double black;
7: color:black;
8: background-color:white;
9: text-align:left;
10: }
11:
12: name {
13: display:block;
14: font-family:Verdana, Arial;
15: font-size:18pt;
16: font-weight:bold;
17: }
18:
19: address {
20: display:block;
21: font-family:Verdana, Arial;
22: font-size:14pt;
23: }
24:
25: city, state, zip {
26: display:inline;
27: font-family:Verdana, Arial;
28: font-size:14pt;
29: }
30:
31: phone, email, company, notes {
32: display:none;
33: }
This style sheet relies on familiar style properties that you learned about in this tutorial. Each relevant element in the Contacts document (contact, name, address, city, state, zip, phone, email, company, and notes) is styled in the style sheet so that its display parameters are clearly stated. A border is established around the contact element (line 6), which contains the remaining elements. The other important code to notice is the code that hides the phone, email, company, and notes elements so that they aren't displayed (lines 3133). This style sheet results in the contacts being displayed as a list of mailing addresses that easily could be printed out as address labels (see Figure 10.1).
Figure 10.1. The Contacts example document is displayed in Opera using the contacts.css style sheet.
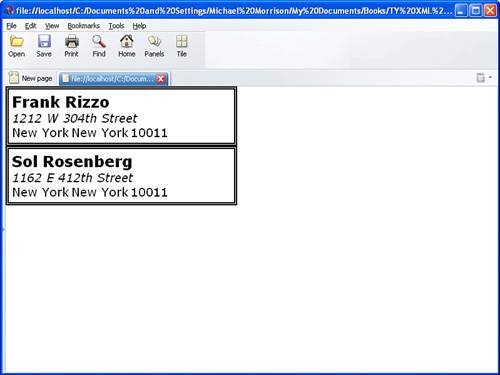
Although the contacts.css style sheet is relatively simple in structure, it is nonetheless a good example of how CSS can be used to format and position XML content on a page for viewing.