Use Sort Text Feature
To remove duplicates from a list, you can use Word's built-in sorting feature to arrange similar entries together and then delete them manually. Follow these steps to sort a list and remove duplicate entries:
- Select the list.
- Go to the
Hometab in the ribbon. - Click
Sortin theParagraph.
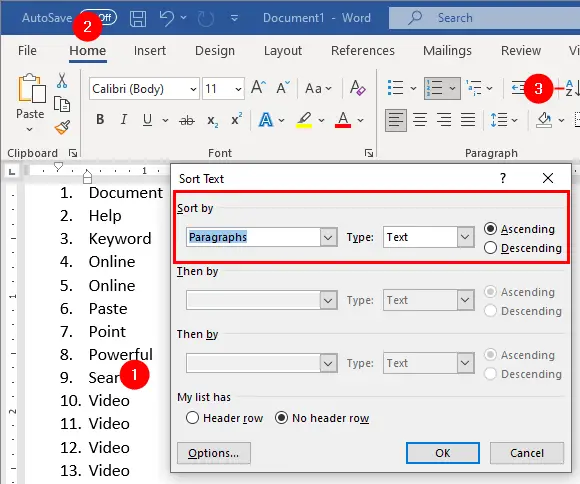
The "Sort Text" dialog box will display. Make sure the following options are selected:
- "Sort by" is set to
Paragraphsand - The "Type" is set to
Text
Click OK to close the dialog.
After sorting, all the duplicate entries will be grouped together. Scroll through the list and manually delete any duplicate entries.
Use Find and Replace
A more efficient and reliable way to remove duplicates is needed when dealing with a large list of items. The previous method may work for a small list, but it is not suitable for a large list due to the significant time it consumes and the potential risk of overlooking duplicate entries.
Regular expressions to the rescue again! You can use the "Find and Replace" feature with wildcards to remove duplicate entries from a list. See following steps:
- First, Sort the list to arrange similar entries together.
- Then, go to the
Hometab in the ribbon. - Press
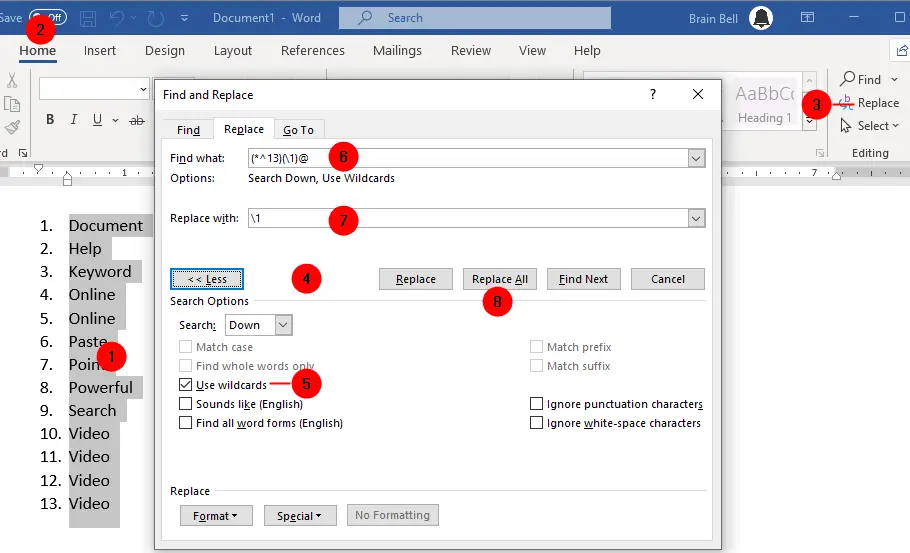
CTRL+Hor clickReplacein theEditinggroup. - In the "Find and Replace" dialog box that opens, click on the
Morebutton to expand the box. - Check the
Use wildcardsbox. - In the "Find what" field, enter the
(*^13)(\1)@wildcard pattern. - In the "Replace with" field, enter
\1. - Click the
Replace Allbutton to remove all duplicate entries in the document.
Word will show you the number of replacements made. This method uses Word's wildcard search feature to identify and remove duplicate entries based on the pattern defined. See how it works:
*represents any text.^13represents a paragraph mark (carriage return).\1identifies a recurrence of the previous expressionin this case, any sequence of characters followed by a carriage return (represented by the code^13).@makes Word find one or more occurrences of the repeated item.
So the expression (*^13)(\1)@ finds a paragraph that is repeated by itself one or more times, and the replacement \1 replaces what is found (the repeated paragraph or paragraphs) with the paragraph itself.