This tutorial covers the following topics:
Reading CSV Files
This tutorial shows how to extract the values from a CSV file into a multidimensional associative array using fopen() and fgetcsv() functions. The fgetcsv() function works similar to the fgets() but it converts the line into an array, separating the contents at a comma (or any other character). Visit Parse the CSV String tutorial if you want to parse a string instead of a CSV file.
Example: Reading CSV File
The sample file contains the following data as comma-separated values:
a,b,c d,e,f g,h,i
- Next, create a PHP script and use the fopen() function to open file.csv in read mode.
- Create an empty array,
$lines, to store the values that will be extracted from the file. - Create the while loop and use
!feof($fp)as the condition. - Use the
fgetcsv()function to extract the lines from the file as an array, and assign them to$linesarray:
<?php
$fp = fopen('file.csv', 'r');
$lines = array();
while (!feof($fp)) {
$lines[] = fgetcsv($fp);
}
fclose($fp);
echo '<pre>';
print_r($lines);
The preceding code prints the following data on the browser:
Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[0] => a
[1] => b
[2] => c
)
[1] => Array
(
[0] => d
[1] => e
[2] => f
)
[2] => Array
(
[0] => g
[1] => h
[2] => i
)
)
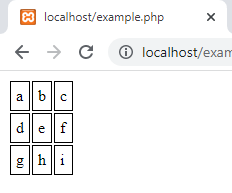
Example: Converting CSV File into HTML Table
<style>td {border: 1px solid black;padding:5px}</style>
<table>
<?php
$fp = fopen('file.csv', 'r');
while (!feof($fp)) {
$row = fgetcsv($fp);
echo '<tr>';
foreach ($row as $cell)
echo "<td>$cell</td>";
echo "</tr>\n";
}
fclose($fp);
?>
<table>
The code reads in a CSV file and outputs it as an HTML table, it displays the following output on the browser:
Example: Reading from a tab delimited file
By default, the fgetcsv() function uses the comma as the field delimiter. To read a tab-separated file, specify the “\t” as the delimiter in the third parameter for fgetcsv():
<?php
$fp = fopen('file.csv', 'r');
$lines = array();
while (!feof($fp)) {
$lines[] = fgetcsv($fp, null, "\t");
}
fclose($fp);
echo '<pre>';
print_r($lines);
fgetcsv()
<?php
//Syntax
fgetcsv(
resource $stream,
?int $length = null,
string $separator = ",",
string $enclosure = "\"",
string $escape = "\\"
): array|false
The fgetcsv function takes the following parameters:
- $stream: The file pointer.
- $length: (optional) Define the maximum length of a line in the CSV file you want to extract the remaining data will get truncated.
- $separator: (optional) The field separator (delimiter), the default value is the comma.
- $enclosure: (optional) Set the field enclosure character.
- $escape: (optional) Set the escape character. The default is a backslash.
Writing to a CSV File
For writing CSV files, PHP offers a sister function, fputcsv(). You provide a file pointer and an array of values, and PHP does the rest, including escaping special characters.
<?php
$data = array(
array('April 2022', '19,720,597', '1,310,181'),
array('January 2022', '18,455,683', '1,317,871'),
array('December 2022', '17,826,404', '1,318,739')
);
if ($fp = fopen('file.csv', 'w')) {
foreach ($data as $line) {
fputcsv($fp, $line);
}
fclose($fp);
echo 'CSV written.';
} else {
echo 'Cannot open file.';
}
This code creates the file file.csv with the following contents:
"April 2022","19,720,597","1,310,181" "January 2022","18,455,683","1,317,871" "December 2022","17,826,404","1,318,739"
Example: Writing to a tab-delimited file
By default, the fputcsv() function uses the comma as the field delimiter. To write a tab-separated file, specify the “\t” as the delimiter in the third parameter:
<?php
$data = array(
array('April 2022', '19,720,597', '1,310,181'),
array('January 2022', '18,455,683', '1,317,871'),
array('December 2022', '17,826,404', '1,318,739')
);
if ($fp = fopen('file.csv', 'w')) {
foreach ($data as $line) {
fputcsv($fp, $line, "\t");
}
fclose($fp);
echo 'CSV written.';
} else {
echo 'Cannot open file.';
}
This code creates the file file.csv with the following contents:
"April 2022" 19,720,597 1,310,181 "January 2022" 18,455,683 1,317,871 "December 2022" 17,826,404 1,318,739
fputcsv
<?php
fputcsv(
resource $stream,
array $fields,
string $separator = ",",
string $enclosure = "\"",
string $escape = "\\",
string $eol = "\n"
): int|false
The fputcsv function returns the length of the written string or false on failure, it takes the following parameters:
$stream: The file pointer opened by fopen().$fields: An array of strings.$separator: (optional) Field delimiter, the default value is a comma.$enclosure: (optional) Filed enclosure, the default value is a double quotation mark.$escape: (optional) Define the escape character.$eol: (optional) Define a custom End of Line sequence.
Working with Files in PHP:
- Returning or Downloading Files with an HTTP Request
- Reading a File into a String or Array
- PHP Opening and Closing Files
- Reading files by line or by character
- Writing and appending to files
- Reading and Writing CSV Files
- Parsing INI Files and Strings
- Check File Type (whether a file is a directory or a file)
- Understanding file Permissions in PHP
- Reading Information About Files in PHP
- Copying, Moving and Deleting Files in PHP
- Reading Directories Contents in PHP
- Browse directories recursively
- Zipping and Unzipping a File with Zlib and Bzip2
- Zip and Unzip Archives with ZipArchive
- Using Relative Paths for File Access