To begin, insert a bar or line chart using some data similar to that shown in the figure:
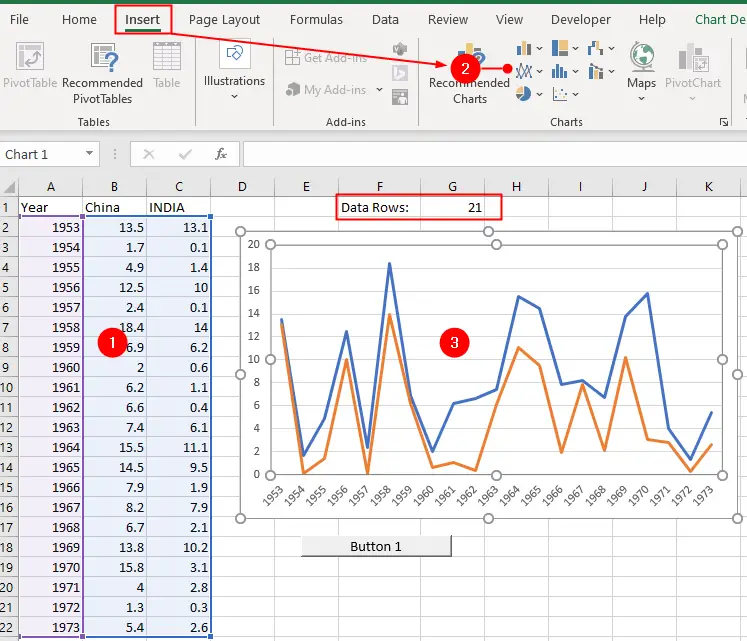
The value entered in cell G1, labeled “Data Rows”, dictates the number of records displayed on the chart. The value in cell G1 will be used by named ranges that we create in the next step.
2. Create Dynamic Named Ranges
Next, create a three dynamic named ranges by selecting Formulas » Define Name and repeating the following steps:
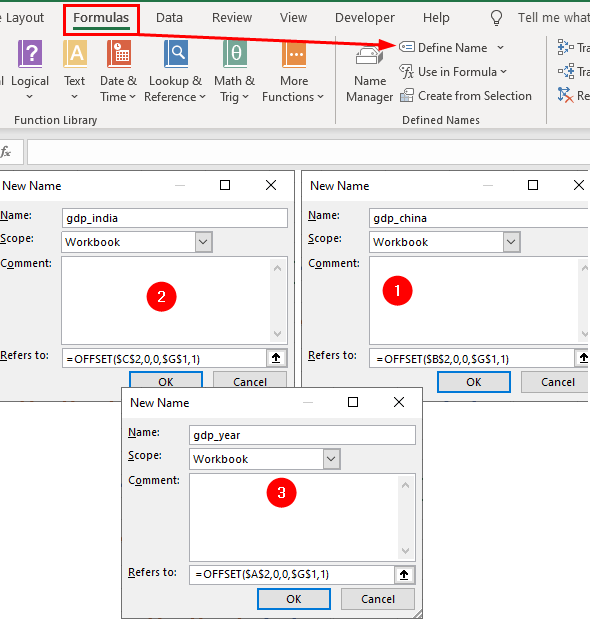
- In the
Name:box typegdp_chinaand
in theRefers to:box, type=OFFSET($B$2,0,0,$G$1,1) - In the
Name:box typegdp_indiaand
in theRefers to:box, type=OFFSET($C$2,0,0,$G$1,1) - In the
Name:box typegdp_yearand
in theRefers to:box, type=OFFSET($A$2,0,0,$G$1,1)
Read Create Scrollable Charts tutorial to learn more about the dynamic ranges.
3. Use Named Ranges in Data Series
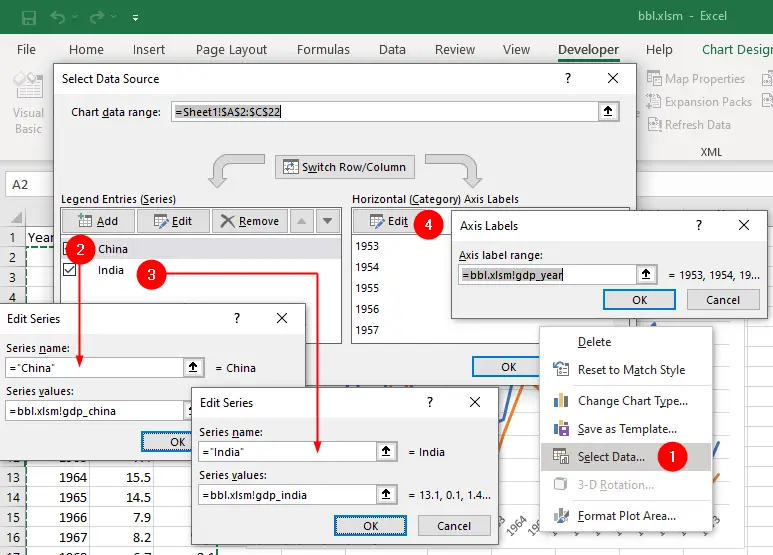
- Right click on the chart and click
Select Dataoption from the context menu.
Remove all existing entries from the Legend Entries (Series) tab except China and India. - Select
Chinaand clickEditbutton, the Edit Series dialog appears:
typeChinain the Series name box
type=workbookName.xlsm!gdp_chinain the Series values box
click OK. - Select
Indiaand clickEditbutton, the Edit Series dialog appears:
typeIndiain the Series name box
type=workbookName.xlsm!gdp_indiain the Series values box
click OK. - Click Edit button in Horizontal (Category) Axis Labels tab. The Axis Labels dialog box appears.
type=workbookName.xlsm!gdp_yearin the Axis label range box and
click OK. - Again click OK button to close the Select Data Source dialog box.
4. Create Macros to Animate Chart Progress
Next we create a macro that will change the value of cell G1 dynamically. Press Alt + F11 to open the Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) editor and go to Insert > Module to insert a new module.
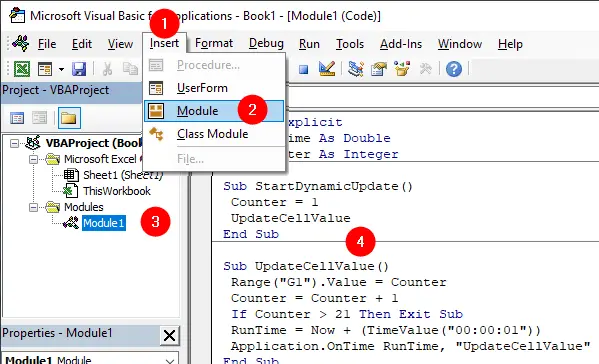
Copy and paste the following code into the module window:
Option Explicit
Dim RunTime As Double
Dim Counter As Integer
Sub StartDynamicUpdate()
Counter = 1
UpdateCellValue
End Sub
Sub UpdateCellValue()
Range("G1").Value = Counter
Counter = Counter + 1
If Counter > 21 Then Exit Sub
RunTime = Now + (TimeValue("00:00:01"))
Application.OnTime RunTime, "UpdateCellValue"
End SubThis code will update the value of cell G1 once in a second, starting from 1 and stopping when the value reaches 21. Adjust the interval (TimeValue("00:00:01")) if you want to change the update frequency.
Close the VBA editor.
5. Run Your VBA Code To Update Chart Data Dynamically
Once your macro is saved, you can run it by going back to the Developer tab, clicking on Macros, selecting the macro you want to run from the list, and clicking Run. Alternatively, press ALT+F8 shortcut key select the macro you want to run e.g. StartDynamicUpdate.
Or you can connect the VBA code to a button, to do so follow these steps:
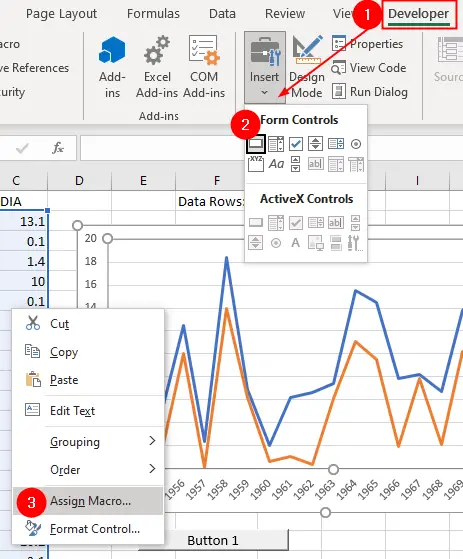
- Go to the
Developertab. If you don’t see theDevelopertab, you may need to enable Developer tab in Excel’s options. - Click on the
Insertdrop-down menu in theControlsgroup and select theButton(Form Control) option. Click and drag to draw the button on your worksheet. - Right-click on the button you inserted and select
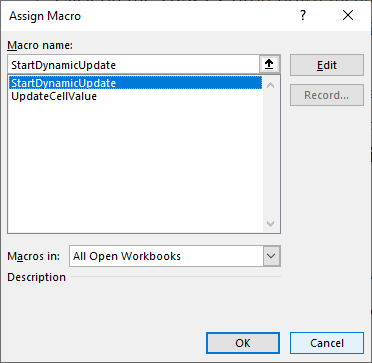
Assign Macro. - In the
Assign Macrodialog box, you should see the name of the macro you created (e.g.,StartDynamicUpdate). Select the macro and clickOK. - Close the dialog box.
Now, when you click the button, the StartDynamicUpdate macro will be executed, which will initiate the dynamic update process.